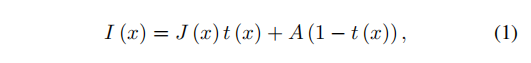文章目录
- 前言
- 一、MSCN-Net多尺度卷积神经网络去雾(非端到端)
-
- 1.网络结构图
- 2.估计传输图代码
- 3.利用传输图和假设环境光去雾公式和代码
- 二、端到端去雾AOD-Net
-
- 1.公式推理和网络结构图
- 2.代码
- 三、DCP-Net密集连接金字塔去雾网络(端到端)
-
- 1.网络结构图
- 2.估计环境光子网络代码
- 3.估计传输图子网络代码
- 4.联合去雾网络代码
- 四、FFA-Net特征注意融合网络去雾(端到端)
-
- 1.总体网络结构图
- 2.注意力机制结构图和代码
- 3.基础块结构图和代码
- 4.总体网络结构图和代码
- 五、门控上下文聚合网络GCA-Net去雾去雨(端到端)
-
- 1.网络结构图
- 2.分割和共享卷积代码
- 3.改进的空洞卷积
- 4.总体网络结构图和代码
- 六、GridDehazeNet注意力的多尺度图像去雾网络(端到端)
-
- 1.网络模块以及总体网络结构图
- 2.RBD模块和上/下采样结构图及代码
- 3.总体结构图及代码
- 七、MSBDN-DFF密集特征融合多尺度去雾网络(端到端)
-
- 1.网络模块以及总体网络结构图和基础模块代码
- 2.DFF密集特征融合结构图和代码
- 3.SOS boosting module结构图和代码
- 4.剩余总体结构图和代码
- 八、Transformer去雾文献(无代码只有网络结构图)
-
- 1.U2-Former 一个用于图像恢复的嵌套的u形Transformer
- 2.Hybrid Local-Global Transformer混合局部全局Transformer
- 2.读入数据
- 总结
前言
记录各种文献中去雾网络的结构和代码
一、MSCN-Net多尺度卷积神经网络去雾(非端到端)
2016年文献
1.网络结构图
2.估计传输图代码
代码如下(示例):
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import math
class dehaze_net(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(dehaze_net, self).__init__()# 公共部分池化上采样激活self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)self.upsample = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()# 粗网的卷积层 卷积核为11、9、7、3self.conv1_1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 5, (11, 11), 1, 5)self.conv1_2 = nn.Conv2d(5, 5, (9, 9), 1, 4)self.conv1_3 = nn.Conv2d(5, 10, (7, 7), 1, 3)self.conv1_4 = nn.Conv2d(10, 1, (3, 3), 1, 1)# 粗网的卷积层 卷积核为7、5、3、1self.conv2_1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 6, (7, 7), 1, 3)self.conv2_2 = nn.Conv2d(7, 5, (5, 5), 1, 2)self.conv2_3 = nn.Conv2d(5, 10, (3, 3), 1, 1)self.conv2_4 = nn.Conv2d(10, 1, (1, 1), 1, 0)def forward(self, x):source = []source.append(x)# 细网# bs 3 320 240 -> bs 5 160 120 -> bs 5 320 240x1 = self.upsample(self.pool(self.conv1_1(x)))# print(x1.shape[0], x1.shape[1], x1.shape[2], x1.shape[3], )# bs 5 320 240 -> bs 5 160 120 -> bs 5 320 240x2 = self.upsample(self.pool(self.conv1_2(x1)))# bs 5 320 240 -> bs 10 160 120 -> bs 10 320 240x3 = self.upsample(self.pool(self.conv1_3(x2)))# bs 10 320 240 -> bs 1 320 240x4 = self.sigmoid(self.conv1_4(x3))# 粗网# bs 3 320 240 -> bs 6 160 120 -> bs 6 320 240x5 = self.upsample(self.pool(self.conv2_1(x)))# bs 6 320 240 -> bs 7 320 240c = torch.cat((x5, x4), dim=1)# bs 7 320 240 -> bs 5 160 120 -> bs 5 320 240x6 = self.upsample(self.pool(self.conv2_2(c)))# bs 5 320 240 -> bs 10 160 120 -> bs 10 320 240x7 = self.upsample(self.pool(self.conv2_3(x6)))# bs 10 320 240 -> bs 1 320 240x8 = self.sigmoid(self.conv2_4(x7))# 返回单通道传输图return x8
3.利用传输图和假设环境光去雾公式和代码
场景传输图 t(x):采用粗尺度估计网络后采用细尺度网络精炼可得
环境光 A:取传输图中最暗的前0.1%的像素点值

代码如下(示例):
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision
import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
import torch.optim
import cv2
import os
import sys
import argparse
import time
import dataloader
import net
import numpy as np
from torchvision import transforms
from PIL import Image
import glob# 从雾图获取环境光
def get_airlight(hzimg, transMap):airlight = np.zeros(hzimg.shape)kernel = np.ones((15,15), np.uint8)for i in range(3):img = cv2.erode(hzimg[:, :, i], kernel, iterations = 1)airlight[:, :, i] = np.amax(img)return airlight# 通过环境光和投射图利用公式得到去雾霾图
def clearImg(hzimg, transMap):airlight = get_airlight(hzimg, transMap)clearImg = np.zeros(hzimg.shape)# transMap = transMap.reshape((transMap.shape[0], transMap.shape[1]))# 小于0.1的值取0.1constant_matrix = np.ones_like(transMap)*0.1clearImg[:, :, 0] = (hzimg[:, :, 0]-airlight[:, :, 0])/np.maximum(constant_matrix[:, :, 0], transMap[:, :, 0]) + airlight[:, :, 0]clearImg[:, :, 1] = (hzimg[:, :, 1]-airlight[:, :, 1])/np.maximum(constant_matrix[:, :, 1], transMap[:, :, 1]) + airlight[:, :, 1]clearImg[:, :, 2] = (hzimg[:, :, 2]-airlight[:, :, 2])/np.maximum(constant_matrix[:, :, 2], transMap[:, :, 2]) + airlight[:, :, 2]clearImg[clearImg < 0.0] = 0.0clearImg[clearImg > 1.0] = 1.0return clearImg
# 输入:待去雾霾图片路径列表 得到:传输图并保存在trans文件夹下
def dehaze_image(image_path):# 雾霾图片归一化转换为32位浮点型张量data_hazy = Image.open(image_path)data_hazy = (np.asarray(data_hazy)/255.0)data_hazy = torch.from_numpy(data_hazy).float()# 调整通道从 h w c ->n c h wdata_hazy = data_hazy.permute(2,0,1)# 添加一个维度 ndata_hazy = data_hazy.cuda().unsqueeze(0)dehaze_net = net.dehaze_net().cuda()# 加载训练好的模型dehaze_net.load_state_dict(torch.load('snapshots/dehazer.pth'))# 得到模型去雾后的图片 这里表示传输图trans_image = dehaze_net(data_hazy)# 传输图并保存在trans文件夹下# torchvision.utils.save_image(torch.cat((data_hazy, trans_image),0), "results/" + image_path.split("\\")[-1])torchvision.utils.save_image(trans_image, "trans/" + image_path.split("\\")[-1])def genclean():trans_path = 'I://Program Files//project//defog//Template//trans//canyon.png'deha_path = 'I://Program Files//project//defog//Template//test_images//canyon.png'deha = cv2.imread(deha_path)deha = deha.astype('float64') / 255trans = cv2.imread(trans_path)trans = trans.astype('float64') / 255claer = clearImg(deha, trans)cv2.imwrite("./clear/dehaze.jpg", claer * 255)print("clear done!")if __name__ == '__main__':# gentrans()genclean()
二、端到端去雾AOD-Net
2017年文献
1.公式推理和网络结构图
2.代码
代码如下(示例):
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import math# 定义网络结构
class dehaze_net(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(dehaze_net, self).__init__()# inplace=True 输入和输出地址相同self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)# 输入通道 输出通道 卷积核尺寸 步长 paddingself.e_conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3,3,1,1,0,bias=True)self.e_conv2 = nn.Conv2d(3,3,3,1,1,bias=True)self.e_conv3 = nn.Conv2d(6,3,5,1,2,bias=True)self.e_conv4 = nn.Conv2d(6,3,7,1,3,bias=True)self.e_conv5 = nn.Conv2d(12,3,3,1,1,bias=True)def forward(self, x):source = []source.append(x)# input:3*480*640 -> 3*480*640 1*1 3*3x1 = self.relu(self.e_conv1(x))x2 = self.relu(self.e_conv2(x1))# input:3*480*640 -> 6*480*640 x1+x2concat1 = torch.cat((x1,x2), 1)# input:6*480*640 -> 3*480*640 5*5x3 = self.relu(self.e_conv3(concat1))# input:3*480*640 -> 6*480*640 x2+x3concat2 = torch.cat((x2, x3), 1)# input:6*480*640 -> 3*480*640 7*7x4 = self.relu(self.e_conv4(concat2))# input:3*480*640 -> 12*480*640 x1+x2+x3+x4concat3 = torch.cat((x1,x2,x3,x4),1)# input:12*480*640 -> 3*480*640 3*3x5 = self.relu(self.e_conv5(concat3))# 代入公式:J(x)=K(x)*I(x)-K(x)+bclean_image = self.relu((x5 * x) - x5 + 1)return clean_image
三、DCP-Net密集连接金字塔去雾网络(端到端)
2018年文献
1.网络结构图
该网络包含两个生成器,分别用于生成传输率图和大气光,再通过大气散射模型产生去雾图。

2.估计环境光子网络代码
代码如下(示例):
import torch
import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo
from collections import OrderedDict
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo
from collections import OrderedDict
import torchvision.models as models
from torch.autograd import Variable# 估计环境光
# 编码模块
def conv_block(in_dim,out_dim):return nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_dim,in_dim,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1),nn.ELU(True),nn.Conv2d(in_dim,in_dim,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1),nn.ELU(True),nn.Conv2d(in_dim,out_dim,kernel_size=1,stride=1,padding=0),# 平均池化下采样nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2,stride=2))# 解码模块
def deconv_block(in_dim,out_dim):return nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_dim,out_dim,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1),nn.ELU(True),nn.Conv2d(out_dim,out_dim,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1),nn.ELU(True),# 上采样nn.UpsamplingNearest2d(scale_factor=2))# 卷积块步长=1
def blockUNet1(in_c, out_c, name, transposed=False, bn=False, relu=True, dropout=False):block = nn.Sequential()if relu:block.add_module('%s.relu' % name, nn.ReLU(inplace=True))else:block.add_module('%s.leakyrelu' % name, nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True))if not transposed:block.add_module('%s.conv' % name, nn.Conv2d(in_c, out_c, 3, 1, 1, bias=False))else:block.add_module('%s.tconv' % name, nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_c, out_c, 3, 1, 1, bias=False))if bn:block.add_module('%s.bn' % name, nn.BatchNorm2d(out_c))if dropout:block.add_module('%s.dropout' % name, nn.Dropout2d(0.5, inplace=True))return block# 卷积块步长=2为下采样
def blockUNet(in_c, out_c, name, transposed=False, bn=False, relu=True, dropout=False):block = nn.Sequential()if relu:block.add_module('%s.relu' % name, nn.ReLU(inplace=True))else:block.add_module('%s.leakyrelu' % name, nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True))if not transposed:block.add_module('%s.conv' % name, nn.Conv2d(in_c, out_c, 4, 2, 1, bias=False))else:block.add_module('%s.tconv' % name, nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_c, out_c, 4, 2, 1, bias=False))if bn:block.add_module('%s.bn' % name, nn.BatchNorm2d(out_c))if dropout:block.add_module('%s.dropout' % name, nn.Dropout2d(0.5, inplace=True))return block# unet:256->1->256 无ssp input=output=3 用来估计环境光
class G2(nn.Module):def __init__(self, input_nc, output_nc, nf):super(G2, self).__init__()# input is 256 x 256layer_idx = 1name = 'layer%d' % layer_idxlayer1 = nn.Sequential()layer1.add_module(name, nn.Conv2d(input_nc, nf, 4, 2, 1, bias=False))# input is 128 x 128layer_idx += 1name = 'layer%d' % layer_idxlayer2 = blockUNet(nf, nf*2, name, transposed=False, bn=True, relu=False, dropout=False)# input is 64 x 64layer_idx += 1name = 'layer%d' % layer_idxlayer3 = blockUNet(nf*2, nf*4, name, transposed=False, bn=True, relu=False, dropout=False)# input is 32layer_idx += 1name = 'layer%d' % layer_idxlayer4 = blockUNet(nf*4, nf*8, name, transposed=False, bn=True, relu=False, dropout=False)# input is 16layer_idx += 1name = 'layer%d' % layer_idxlayer5 = blockUNet(nf*8, nf*8, name, transposed=False, bn=True, relu=False, dropout=False)# input is 8layer_idx += 1name = 'layer%d' % layer_idxlayer6 = blockUNet(nf*8, nf*8, name, transposed=False, bn=True, relu=False, dropout=False)# input is 4layer_idx += 1name = 'layer%d' % layer_idxlayer7 = blockUNet(nf*8, nf*8, name, transposed=False, bn=True, relu=False, dropout=False)# input is 2 x 2layer_idx += 1name = 'layer%d' % layer_idxlayer8 = blockUNet(nf*8, nf*8, name, transposed=False, bn=True, relu=False, dropout=False)## NOTE: decoder# input is 1name = 'dlayer%d' % layer_idxd_inc = nf*8dlayer8 = blockUNet(d_inc, nf*8, name, transposed=True, bn=False, relu=True, dropout=True)#import pdb; pdb.set_trace()# input is 2layer_idx -= 1name = 'dlayer%d' % layer_idxd_inc = nf*8*2dlayer7 = blockUNet(d_inc, nf*8, name, transposed=True, bn=True, relu=True, dropout=True)# input is 4layer_idx -= 1name = 'dlayer%d' % layer_idxd_inc = nf*8*2dlayer6 = blockUNet(d_inc, nf*8, name, transposed=True, bn=True, relu=True, dropout=True)# input is 8layer_idx -= 1name = 'dlayer%d' % layer_idxd_inc = nf*8*2dlayer5 = blockUNet(d_inc, nf*8, name, transposed=True, bn=True, relu=True, dropout=False)# input is 16layer_idx -= 1name = 'dlayer%d' % layer_idxd_inc = nf*8*2dlayer4 = blockUNet(d_inc, nf*4, name, transposed=True, bn=True, relu=True, dropout=False)# input is 32layer_idx -= 1name = 'dlayer%d' % layer_idxd_inc = nf*4*2dlayer3 = blockUNet(d_inc, nf*2, name, transposed=True, bn=True, relu=True, dropout=False)# input is 64layer_idx -= 1name = 'dlayer%d' % layer_idxd_inc = nf*2*2dlayer2 = blockUNet(d_inc, nf, name, transposed=True, bn=True, relu=True, dropout=False)# input is 128layer_idx -= 1name = 'dlayer%d' % layer_idxdlayer1 = nn.Sequential()d_inc = nf*2dlayer1.add_module('%s.relu' % name, nn.ReLU(inplace=True))dlayer1.add_module('%s.tconv' % name, nn.ConvTranspose2d(d_inc, output_nc, 4, 2, 1, bias=False))dlayer1.add_module('%s.tanh' % name, nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True))self.layer1 = layer1self.layer2 = layer2self.layer3 = layer3self.layer4 = layer4self.layer5 = layer5self.layer6 = layer6self.layer7 = layer7self.layer8 = layer8self.dlayer8 = dlayer8self.dlayer7 = dlayer7self.dlayer6 = dlayer6self.dlayer5 = dlayer5self.dlayer4 = dlayer4self.dlayer3 = dlayer3self.dlayer2 = dlayer2self.dlayer1 = dlayer1def forward(self, x):out1 = self.layer1(x)out2 = self.layer2(out1)out3 = self.layer3(out2)out4 = self.layer4(out3)out5 = self.layer5(out4)out6 = self.layer6(out5)out7 = self.layer7(out6)out8 = self.layer8(out7)dout8 = self.dlayer8(out8)dout8_out7 = torch.cat([dout8, out7], 1)dout7 = self.dlayer7(dout8_out7)dout7_out6 = torch.cat([dout7, out6], 1)dout6 = self.dlayer6(dout7_out6)dout6_out5 = torch.cat([dout6, out5], 1)dout5 = self.dlayer5(dout6_out5)dout5_out4 = torch.cat([dout5, out4], 1)dout4 = self.dlayer4(dout5_out4)dout4_out3 = torch.cat([dout4, out3], 1)dout3 = self.dlayer3(dout4_out3)dout3_out2 = torch.cat([dout3, out2], 1)dout2 = self.dlayer2(dout3_out2)dout2_out1 = torch.cat([dout2, out1], 1)dout1 = self.dlayer1(dout2_out1)return dout13.估计传输图子网络代码
代码如下(示例):
# 估计传输图
# 残差块 相隔两次卷积进行add
class BottleneckBlock(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, dropRate=0.0):super(BottleneckBlock, self).__init__()inter_planes = out_planes * 4self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1,padding=0, bias=False)self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(inter_planes)self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(inter_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1,padding=1, bias=False)self.droprate = dropRatedef forward(self, x):out = self.conv1(self.relu(self.bn1(x)))if self.droprate > 0:out = F.dropout(out, p=self.droprate, inplace=False, training=self.training)out = self.conv2(self.relu(self.bn2(out)))if self.droprate > 0:out = F.dropout(out, p=self.droprate, inplace=False, training=self.training)return torch.cat([x, out], 1)class TransitionBlock(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, dropRate=0.0):super(TransitionBlock, self).__init__()self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)self.conv1 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1,padding=0, bias=False)self.droprate = dropRatedef forward(self, x):out = self.conv1(self.relu(self.bn1(x)))if self.droprate > 0:out = F.dropout(out, p=self.droprate, inplace=False, training=self.training)return F.upsample_nearest(out, scale_factor=2)# 256->8->256 + ssp 输出3通道
class Dense(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(Dense, self).__init__()############# 256-256 ##############haze_class = models.densenet121(pretrained=True)self.conv0=haze_class.features.conv0self.norm0=haze_class.features.norm0self.relu0=haze_class.features.relu0self.pool0=haze_class.features.pool0############# Block1-down 64-64 ##############self.dense_block1=haze_class.features.denseblock1self.trans_block1=haze_class.features.transition1############# Block2-down 32-32 ##############self.dense_block2=haze_class.features.denseblock2self.trans_block2=haze_class.features.transition2############# Block3-down 16-16 ##############self.dense_block3=haze_class.features.denseblock3self.trans_block3=haze_class.features.transition3############# Block4-up 8-8 ############### 残差块输入通道数512+输出通道数156=768self.dense_block4=BottleneckBlock(512,256)# 上采样8->16self.trans_block4=TransitionBlock(768,128)############# Block5-up 16-16 ##############self.dense_block5=BottleneckBlock(384,256)# 上采样16->32self.trans_block5=TransitionBlock(640,128)############# Block6-up 32-32 ##############self.dense_block6=BottleneckBlock(256,128)# 上采样32->64self.trans_block6=TransitionBlock(384,64)############# Block7-up 64-64 ##############self.dense_block7=BottleneckBlock(64,64)# 上采样64->128self.trans_block7=TransitionBlock(128,32)## 128 X 128############# Block8-up c ##############self.dense_block8=BottleneckBlock(32,32)# 上采样128->256self.trans_block8=TransitionBlock(64,16)self.conv_refin=nn.Conv2d(19,20,3,1,1)self.tanh=nn.Tanh()self.conv1010 = nn.Conv2d(20, 1, kernel_size=1,stride=1,padding=0) # 1mmself.conv1020 = nn.Conv2d(20, 1, kernel_size=1,stride=1,padding=0) # 1mmself.conv1030 = nn.Conv2d(20, 1, kernel_size=1,stride=1,padding=0) # 1mmself.conv1040 = nn.Conv2d(20, 1, kernel_size=1,stride=1,padding=0) # 1mmself.refine3= nn.Conv2d(20+4, 3, kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1)# self.refine3= nn.Conv2d(20+4, 3, kernel_size=7,stride=1,padding=3)self.upsample = F.upsample_nearestself.relu=nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)def forward(self, x):## 256x256->64 X 64x0=self.pool0(self.relu0(self.norm0(self.conv0(x))))## 64 X 64 残差结构x1=self.dense_block1(x0)# print x1.size()## 64 X 64->32 X 32x1=self.trans_block1(x1)### 32x32->16 X 16x2=self.trans_block2(self.dense_block2(x1))# print x2.size()### 16 X 16->8 X 8x3=self.trans_block3(self.dense_block3(x2))# x3=Variable(x3.data,requires_grad=True)## 8 X 8->16 X 16x4=self.trans_block4(self.dense_block4(x3))# 堆叠x42=torch.cat([x4,x2],1)## 16 X 16->32 X 32x5=self.trans_block5(self.dense_block5(x42))# 堆叠x52=torch.cat([x5,x1],1)## 32 X 32->64 X 64x6=self.trans_block6(self.dense_block6(x52))## 64 X 64->128 X 128x7=self.trans_block7(self.dense_block7(x6))## 128 X 128->256 X 256x8=self.trans_block8(self.dense_block8(x7))# print x8.size()# print x.size()# 堆叠x8=torch.cat([x8,x],1)# print x8.size()x9=self.relu(self.conv_refin(x8))shape_out = x9.data.size()# print(shape_out)shape_out = shape_out[2:4]x101 = F.avg_pool2d(x9, 32)x102 = F.avg_pool2d(x9, 16)x103 = F.avg_pool2d(x9, 8)x104 = F.avg_pool2d(x9, 4)x1010 = self.upsample(self.relu(self.conv1010(x101)), size=shape_out)x1020 = self.upsample(self.relu(self.conv1020(x102)), size=shape_out)x1030 = self.upsample(self.relu(self.conv1030(x103)), size=shape_out)x1040 = self.upsample(self.relu(self.conv1040(x104)), size=shape_out)dehaze = torch.cat((x1010, x1020, x1030, x1040, x9), 1)dehaze = self.tanh(self.refine3(dehaze))return dehaze
4.联合去雾网络代码
代码如下(示例):
class dehaze(nn.Module):def __init__(self, input_nc, output_nc, nf):super(dehaze, self).__init__()# unet:256->1->256 + ssp 输出通道3 备用估计传输率self.tran_est=G(input_nc=3,output_nc=3, nf=64)# unet:256->1->256 无ssp 输出通道3 用来估计环境光self.atp_est=G2(input_nc=3,output_nc=3, nf=8)# unet+Dense:256->8->256 + ssp 输出3通道 真正用来估计传输率self.tran_dense=Dense()self.relu=nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True)# self.relu5=nn.ReLU6()self.tanh=nn.Tanh()# 去雾图+雾图 通道数3+3=6self.refine1= nn.Conv2d(6, 20, kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1)self.refine2= nn.Conv2d(20, 20, kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1)# x大于0.1=x 小于0.1=0.1self.threshold=nn.Threshold(0.1, 0.1)self.conv1010 = nn.Conv2d(20, 1, kernel_size=1,stride=1,padding=0) # 1mmself.conv1020 = nn.Conv2d(20, 1, kernel_size=1,stride=1,padding=0) # 1mmself.conv1030 = nn.Conv2d(20, 1, kernel_size=1,stride=1,padding=0) # 1mmself.conv1040 = nn.Conv2d(20, 1, kernel_size=1,stride=1,padding=0) # 1mmself.refine3= nn.Conv2d(20+4, 3, kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1)self.upsample = F.upsample_nearestself.batch1= nn.BatchNorm2d(20)# self.batch2 = nn.InstanceNorm2d(100, affine=True)def forward(self, x):# unet+Dense:256->8->256 + ssp 输出3通道 真正用来估计传输率tran=self.tran_dense(x)# unet:256->1->256 无ssp 输出通道3 用来估计环境光atp= self.atp_est(x)# x = Variable(x.data, requires_grad=True)# zz= torch.abs(self.threshold(tran))zz= torch.abs((tran))+(10**-10)shape_out1 = atp.data.size()# print(shape_out)# shape_out = shape_out[0:5]# atp_mean=torch.mean(atp)# threshold = nn.Threshold(10, 0.95)shape_out = shape_out1[2:4]# 全局最大池化 池化核尺寸等于图片HW 输出为bs c 1 1atp = F.avg_pool2d(atp, shape_out1[2])atp = self.upsample(self.relu(atp),size=shape_out)# print atp.data# atp = threshold(atp)# 去雾公式dehaze= (x-atp)/zz+ atpdehaze2=dehazedehaze=torch.cat([dehaze,x],1)# dehaze=dehaze/(tran+(10**-10))# dehaze=self.relu(self.batch1(self.refine1(dehaze)))# dehaze=self.relu(self.batch1(self.refine2(dehaze)))dehaze=self.relu((self.refine1(dehaze)))dehaze=self.relu((self.refine2(dehaze)))shape_out = dehaze.data.size()# print(shape_out)shape_out = shape_out[2:4]# ssp 不同池化核x101 = F.avg_pool2d(dehaze, 32)x1010 = F.avg_pool2d(dehaze, 32)x102 = F.avg_pool2d(dehaze, 16)x1020 = F.avg_pool2d(dehaze, 16)x103 = F.avg_pool2d(dehaze, 8)x104 = F.avg_pool2d(dehaze, 4)# 恢复池化后的尺寸便于拼接x1010 = self.upsample(self.relu(self.conv1010(x101)),size=shape_out)x1020 = self.upsample(self.relu(self.conv1020(x102)),size=shape_out)x1030 = self.upsample(self.relu(self.conv1030(x103)),size=shape_out)x1040 = self.upsample(self.relu(self.conv1040(x104)),size=shape_out)dehaze = torch.cat((x1010, x1020, x1030, x1040, dehaze), 1)dehaze= self.tanh(self.refine3(dehaze))return dehaze, tran, atp, dehaze2
四、FFA-Net特征注意融合网络去雾(端到端)
2019年文献
1.总体网络结构图
2.注意力机制结构图和代码
# 定义网络结构
def default_conv(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, bias=True):return nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, padding=(kernel_size // 2), bias=bias)# 像素注意力机制
class PALayer(nn.Module):def __init__(self, channel):super(PALayer, self).__init__()self.pa = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(channel, channel // 8, 1, padding=0, bias=True),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(channel // 8, 1, 1, padding=0, bias=True),nn.Sigmoid())def forward(self, x):y = self.pa(x)return x * y# 通道注意力机制
class CALayer(nn.Module):def __init__(self, channel):super(CALayer, self).__init__()# 全局平均池化 C*H*W->C*1*1self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)self.ca = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(channel, channel // 8, 1, padding=0, bias=True),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(channel // 8, channel, 1, padding=0, bias=True),nn.Sigmoid())def forward(self, x):y = self.avg_pool(x)y = self.ca(y)return x * yxt
3.基础块结构图和代码
# 图像浅蓝色正方体B块
class Block(nn.Module):def __init__(self, conv, dim, kernel_size, ):super(Block, self).__init__()self.conv1 = conv(dim, dim, kernel_size, bias=True)self.act1 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)self.conv2 = conv(dim, dim, kernel_size, bias=True)self.calayer = CALayer(dim)self.palayer = PALayer(dim)def forward(self, x):res = self.act1(self.conv1(x))res = res + xres = self.conv2(res)res = self.calayer(res)res = self.palayer(res)res += xreturn res
4.总体网络结构图和代码
def default_conv(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, bias=True):return nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, padding=(kernel_size // 2), bias=bias)
# 图像深蓝色正方体G组
class Group(nn.Module):def __init__(self, conv, dim, kernel_size, blocks):super(Group, self).__init__()modules = [Block(conv, dim, kernel_size) for _ in range(blocks)]modules.append(conv(dim, dim, kernel_size))self.gp = nn.Sequential(*modules)def forward(self, x):res = self.gp(x)res += xreturn res
class FFA(nn.Module):# gps=3 blocks=2def __init__(self, gps, blocks, conv=default_conv):super(FFA, self).__init__()self.gps = gpsself.dim = 64kernel_size = 3# 预处理 BS*3*H*W->BS*64*H*Wpre_process = [conv(3, self.dim, kernel_size)]# 默认3组深蓝assert self.gps == 3self.g1 = Group(conv, self.dim, kernel_size, blocks=blocks)self.g2 = Group(conv, self.dim, kernel_size, blocks=blocks)self.g3 = Group(conv, self.dim, kernel_size, blocks=blocks)self.ca = nn.Sequential(*[# g1+g2+g3=(BS*64*1*1)*3=BS*192*H*W->BS*192*1*1nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1),# BS*192*1*1->BS*12*1*1nn.Conv2d(self.dim * self.gps, self.dim // 16, 1, padding=0),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),# BS*12*1*1->BS*192*1*1nn.Conv2d(self.dim // 16, self.dim * self.gps, 1, padding=0, bias=True),nn.Sigmoid()])self.palayer = PALayer(self.dim)# 后处理两个卷积post_precess = [conv(self.dim, self.dim, kernel_size),conv(self.dim, 3, kernel_size)]self.pre = nn.Sequential(*pre_process)self.post = nn.Sequential(*post_precess)def forward(self, x1):# 预处理 BS*3*H*W->BS*64*H*Wx = self.pre(x1)res1 = self.g1(x)res2 = self.g2(res1)res3 = self.g3(res2)# 通道注意力机得到的权重与每个通道相乘# BS*64*H*W->BS*192*H*W->BS*192*1*1w = self.ca(torch.cat([res1, res2, res3], dim=1))# BS*192*1*1->BS*3*64w = w.view(-1, self.gps, self.dim)[:, :, :, None, None]# BS*64*H*Wout = w[:, 0, ::] * res1 + w[:, 1, ::] * res2 + w[:, 2, ::] * res3# 像素注意力机得到的权重与每个像素相乘 BS*64*H*Wout = self.palayer(out)# BS*64*H*W->BS*3*H*Wx = self.post(out)return x + x1
五、门控上下文聚合网络GCA-Net去雾去雨(端到端)
2019年文献
1.网络结构图
2.分割和共享卷积代码
代码如下(示例):
# SS convolution 分割和共享卷积(separate and shared convolution)
class ShareSepConv(nn.Module):def __init__(self, kernel_size):super(ShareSepConv, self).__init__()# assert条件为假时,报错(卷积核大小必须为奇数)assert kernel_size % 2 == 1, 'kernel size should be odd'self.padding = (kernel_size - 1)//2# 1种1通道kernel_size, kernel_size大小的卷积核# 手动定义卷积核(weight),weight矩阵正中间的元素是1,其余为0weight_tensor = torch.zeros(1, 1, kernel_size, kernel_size)weight_tensor[0, 0, (kernel_size-1)//2, (kernel_size-1)//2] = 1# nn.Parameter:类型转换函数,将一个不可训练的类型Tensor转换成可以训练的类型parameter并将这个parameter绑定到module里self.weight = nn.Parameter(weight_tensor)self.kernel_size = kernel_sizedef forward(self, x):# 获取输入图片的通道数inc = x.size(1)# 根据Share and Separable convolution的定义,复制weights,x的每个通道对应相同的weight,contiguous()函数使得复制后并在内存空间上对齐# .expand自动将原来的张量所有长度为1的维度扩展成所需要的长度,将卷积核转换成(in_c) batch_sizeexpand_weight = self.weight.expand(inc, 1, self.kernel_size, self.kernel_size).contiguous()# 调用F.conv2d进行卷积操作 可以这样理解:nn.Conv2d是[2D卷积层],而F.conv2d是[2D卷积操作]# 参数:x w b str=1 pad 扩张卷积dilation rate=1即不扩张 groups:大于1时卷积核数目变为原来的2分之一return F.conv2d(x, expand_weight,None, 1, self.padding, 1, inc)
3.改进的空洞卷积
代码如下(示例):
# 改进的空洞卷积
class SmoothDilatedResidualBlock(nn.Module):def __init__(self, channel_num, dilation=1, group=1):super(SmoothDilatedResidualBlock, self).__init__()# 在空洞卷积之前先使用SS convolution进行局部信息融合self.pre_conv1 = ShareSepConv(dilation*2-1)# 空洞卷积self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(channel_num, channel_num, 3, 1, padding=dilation, dilation=dilation, groups=group, bias=False)# 归一化层 num_features:来自期望输入的特征数 affine:布尔值,当设为true,给该层添加可学习的仿射变换参数self.norm1 = nn.InstanceNorm2d(channel_num, affine=True)# 在空洞卷积之前先使用SS convolution进行局部信息融合self.pre_conv2 = ShareSepConv(dilation*2-1)# 空洞卷积self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(channel_num, channel_num, 3, 1, padding=dilation, dilation=dilation, groups=group, bias=False)# 归一化层self.norm2 = nn.InstanceNorm2d(channel_num, affine=True)def forward(self, x):y = F.relu(self.norm1(self.conv1(self.pre_conv1(x))))y = self.norm2(self.conv2(self.pre_conv2(y)))# 残差连接return F.relu(x+y)# 残差网络 每两层增加一个捷径,构成一个残差块,此结构图有7个残差块
class ResidualBlock(nn.Module):def __init__(self, channel_num, dilation=1, group=1):super(ResidualBlock, self).__init__()self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(channel_num, channel_num, 3, 1, padding=dilation, dilation=dilation, groups=group, bias=False)self.norm1 = nn.InstanceNorm2d(channel_num, affine=True)self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(channel_num, channel_num, 3, 1, padding=dilation, dilation=dilation, groups=group, bias=False)self.norm2 = nn.InstanceNorm2d(channel_num, affine=True)def forward(self, x):y = F.relu(self.norm1(self.conv1(x)))y = self.norm2(self.conv2(y))return F.relu(x+y)
4.总体网络结构图和代码
class GCANet(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_c=4, out_c=3, only_residual=True):super(GCANet, self).__init__()# Encoder:三层卷积,通道数64,卷积核大小3*3,stride=1,padding=1 output:(bs,64,im_h,im_w)self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_c, 64, 3, 1, 1, bias=False)self.norm1 = nn.InstanceNorm2d(64, affine=True)self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, 3, 1, 1, bias=False)self.norm2 = nn.InstanceNorm2d(64, affine=True)# stride=2的下采样 output:(bs,64,im_h/2,im_w/2)self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, 3, 2, 1, bias=False)self.norm3 = nn.InstanceNorm2d(64, affine=True)# 中间层:7层smooth dilated convolution残差块,空洞率r分别为2,2,2,4,4,4,1,通道数64self.res1 = SmoothDilatedResidualBlock(64, dilation=2)self.res2 = SmoothDilatedResidualBlock(64, dilation=2)self.res3 = SmoothDilatedResidualBlock(64, dilation=2)self.res4 = SmoothDilatedResidualBlock(64, dilation=4)self.res5 = SmoothDilatedResidualBlock(64, dilation=4)self.res6 = SmoothDilatedResidualBlock(64, dilation=4)# 空洞率为1时分离卷积的卷积核为1*1,没有起到信息融合的作用,因此该层退化为一个普通的残差网络self.res7 = ResidualBlock(64, dilation=1)# Gated Fusion Sub-network:学习低,中,高层特征的权重self.gate = nn.Conv2d(64 * 3, 3, 3, 1, 1, bias=True)# Decoder:1层反卷积层将feature map上采样到原分辨率+2层卷积层将feature map还原到原图空间 stride=2的上采样self.deconv3 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(64, 64, 4, 2, 1)self.norm4 = nn.InstanceNorm2d(64, affine=True)self.deconv2 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, 3, 1, 1)self.norm5 = nn.InstanceNorm2d(64, affine=True)# 1*1卷积核进行降维 调整通道数为3self.deconv1 = nn.Conv2d(64, out_c, 1)self.only_residual = only_residualdef forward(self, x):# Encoder前向传播,使用relu激活 低层级信息y = F.relu(self.norm1(self.conv1(x)))y = F.relu(self.norm2(self.conv2(y)))y1 = F.relu(self.norm3(self.conv3(y)))# 中间层y = self.res1(y1)y = self.res2(y)y = self.res3(y)# 中层级信息y2 = self.res4(y)y = self.res5(y2)y = self.res6(y)# 高层级信息y3 = self.res7(y)# Gated Fusion Sub-network output:(bs,3,im_h/2,im_w/2)gates = self.gate(torch.cat((y1, y2, y3), dim=1))# 计算低,中,高层特征的权重 对低,中,高层特征加权求和 output:(bs,64,im_h/2,im_w/2)gated_y = y1 * gates[:, [0], :, :] + y2 * gates[:, [1], :, :] + y3 * gates[:, [2], :, :]# output:(bs,64,im_h,im_w)y = F.relu(self.norm4(self.deconv3(gated_y)))y = F.relu(self.norm5(self.deconv2(y)))if self.only_residual:# output: (bs,3,im_h,im_w)y = self.deconv1(y)else:y = F.relu(self.deconv1(y))return y六、GridDehazeNet注意力的多尺度图像去雾网络(端到端)
2019年文献
1.网络模块以及总体网络结构图
GridDehazeNet包含三个模块:预处理模块,主干模块和后处理模块。

2.RBD模块和上/下采样结构图及代码
代码如下(示例):
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F# --- Build dense --- #
class MakeDense(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, growth_rate, kernel_size=3):super(MakeDense, self).__init__()# in_channels输入通道数 growth_rate输出通道数 论文中为16self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, growth_rate, kernel_size=kernel_size, padding=(kernel_size-1)//2)def forward(self, x):out = F.relu(self.conv(x))# 沿通道维度进行堆叠 通道数等于in_channels+growth_rate=16+16out = torch.cat((x, out), 1)return out# --- Build the Residual Dense Block --- #
class RDB(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, num_dense_layer, growth_rate):""":param in_channels: input channel size:param num_dense_layer: the number of RDB layers:param growth_rate: growth_rate"""super(RDB, self).__init__()_in_channels = in_channelsmodules = []# 一共5层 前四层特征堆叠 最后一层调整通道数for i in range(num_dense_layer):modules.append(MakeDense(_in_channels, growth_rate))_in_channels += growth_rateself.residual_dense_layers = nn.Sequential(*modules)# 用来把堆叠后的通道数恢复到初始通道数16self.conv_1x1 = nn.Conv2d(_in_channels, in_channels, kernel_size=1, padding=0)def forward(self, x):out = self.residual_dense_layers(x)out = self.conv_1x1(out)# 通道数不变对应值相加out = out + xreturn out# --- Downsampling block in GridDehazeNet --- #
class DownSample(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=2):super(DownSample, self).__init__()# 下采样尺寸缩小两倍 通时通道数扩张二倍self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, in_channels, kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=(kernel_size-1)//2)self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, stride*in_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=(kernel_size - 1) // 2)def forward(self, x):out = F.relu(self.conv1(x))out = F.relu(self.conv2(out))return out# --- Upsampling block in GridDehazeNet --- #
class UpSample(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=2):super(UpSample, self).__init__()# 上采样尺寸扩大两倍 同时通道数缩小二倍self.deconv = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels, in_channels, kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=1)self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, in_channels // stride, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=(kernel_size - 1) // 2)def forward(self, x, output_size):out = F.relu(self.deconv(x, output_size=output_size))out = F.relu(self.conv(out))return out
3.总体结构图及代码
# --- Main model --- #
class GridDehazeNet(nn.Module):# 3行6列 RBD中4次通道堆叠 RBD输入16个特征层输出也是16def __init__(self, in_channels=3, depth_rate=16, kernel_size=3, stride=2, height=3, width=6, num_dense_layer=4, growth_rate=16, attention=True):super(GridDehazeNet, self).__init__()# 3行5列RBD 对应主干模块中的绿色块self.rdb_module = nn.ModuleDict()# 2行3列上采样 对应主干模块紫色块self.upsample_module = nn.ModuleDict()# 2行3列下采样 对应主干模块蓝色块self.downsample_module = nn.ModuleDict()self.height = heightself.width = widthself.stride = strideself.depth_rate = depth_rate# coefficient:系数 通道数:depth_rate*stride**(height-1)self.coefficient = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(np.ones((height, width, 2, depth_rate*stride**(height-1)))), requires_grad=attention)# 对应论文中预处理第一个黄色卷积 输入通道3 输出通道16 卷积核尺寸3*3 步长为1 特征图尺寸不变self.conv_in = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, depth_rate, kernel_size=kernel_size, padding=(kernel_size - 1) // 2)# 对应论文中后处理第最后一个黄色卷积 输入通道16 输出通道3 卷积核尺寸3*3 步长为1 特征图尺寸不变self.conv_out = nn.Conv2d(depth_rate, in_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, padding=(kernel_size - 1) // 2)# 对应论文中预处理绿色RBDself.rdb_in = RDB(depth_rate, num_dense_layer, growth_rate)# 对应论文中后处理绿色RBDself.rdb_out = RDB(depth_rate, num_dense_layer, growth_rate)# 3行5列RBD 对应主干模块中的绿色块rdb_in_channels = depth_rate# 3行for i in range(height):# 5列for j in range(width - 1):self.rdb_module.update({'{}_{}'.format(i, j): RDB(rdb_in_channels, num_dense_layer, growth_rate)})# 每一行进一次下采样通道数乘以2 分别为16 32 64rdb_in_channels *= stride# 2行3列下采样 对应主干模块蓝色块_in_channels = depth_ratefor i in range(height - 1):for j in range(width // 2):self.downsample_module.update({'{}_{}'.format(i, j): DownSample(_in_channels)})# 每一行进一次下采样通道数乘以2 分别为16 32 64_in_channels *= stride# 2行3列上采样 对应主干模块紫色块for i in range(height - 2, -1, -1):for j in range(width // 2, width):self.upsample_module.update({'{}_{}'.format(i, j): UpSample(_in_channels)})# 每一行进一次上采样通道数除以2 分别为64 32 16_in_channels //= stridedef forward(self, x):# 预处理中的单步卷积 bs 3 480 640 -> bs 16 480 640inp = self.conv_in(x)# 二维列表 三行012 六列012345x_index = [[0 for _ in range(self.width)] for _ in range(self.height)]i, j = 0, 0# 预处理中的RBD输入 在二维列表中索引为0 0x_index[0][0] = self.rdb_in(inp)# 第0行 索引为12的列 两次RBDfor j in range(1, self.width // 2):x_index[0][j] = self.rdb_module['{}_{}'.format(0, j-1)](x_index[0][j-1])# 第0列 索引为12的两行 进行下采样for i in range(1, self.height):x_index[i][0] = self.downsample_module['{}_{}'.format(i-1, 0)](x_index[i-1][0])# 第1和2行 第2和3列for i in range(1, self.height):for j in range(1, self.width // 2):channel_num = int(2**(i-1)*self.stride*self.depth_rate)# 特征堆叠 12行和23列四个红色交叉点A的堆叠 下采样+RBD# x_index[i][j-1]前一列的rbd 加上 x_index[i-1][j]前一行的下采样x_index[i][j] = self.coefficient[i, j, 0, :channel_num][None, :, None, None] * self.rdb_module['{}_{}'.format(i, j-1)](x_index[i][j-1]) + \self.coefficient[i, j, 1, :channel_num][None, :, None, None] * self.downsample_module['{}_{}'.format(i-1, j)](x_index[i-1][j])# 不同行的上一列是下一列的输入 第3列RBDx_index[i][j+1] = self.rdb_module['{}_{}'.format(i, j)](x_index[i][j])k = j# 45列012行 RBDfor j in range(self.width // 2 + 1, self.width):x_index[i][j] = self.rdb_module['{}_{}'.format(i, j-1)](x_index[i][j-1])# 两行三列右上角的交叉点for i in range(self.height - 2, -1, -1):channel_num = int(2 ** (i-1) * self.stride * self.depth_rate)x_index[i][k+1] = self.coefficient[i, k+1, 0, :channel_num][None, :, None, None] * self.rdb_module['{}_{}'.format(i, k)](x_index[i][k]) + \self.coefficient[i, k+1, 1, :channel_num][None, :, None, None] * self.upsample_module['{}_{}'.format(i, k+1)](x_index[i+1][k+1], x_index[i][k].size())for i in range(self.height - 2, -1, -1):for j in range(self.width // 2 + 1, self.width):channel_num = int(2 ** (i - 1) * self.stride * self.depth_rate)x_index[i][j] = self.coefficient[i, j, 0, :channel_num][None, :, None, None] * self.rdb_module['{}_{}'.format(i, j-1)](x_index[i][j-1]) + \self.coefficient[i, j, 1, :channel_num][None, :, None, None] * self.upsample_module['{}_{}'.format(i, j)](x_index[i+1][j], x_index[i][j-1].size())# 后处理的RBDout = self.rdb_out(x_index[i][j])# 后处理的单步卷积out = F.relu(self.conv_out(out))return out
七、MSBDN-DFF密集特征融合多尺度去雾网络(端到端)
2020年文献
1.网络模块以及总体网络结构图和基础模块代码
包含3个模块Genc,Gres,Gdec其中Dense Feature Fusion Module和SOS boosting module难理解接下来介绍

代码如下(示例):
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from networks.base_networks import Encoder_MDCBlock1, Decoder_MDCBlock1def make_model(args, parent=False):return Net()# 残差块
class make_dense(nn.Module):def __init__(self, nChannels, growthRate, kernel_size=3):super(make_dense, self).__init__()self.conv = nn.Conv2d(nChannels, growthRate, kernel_size=kernel_size, padding=(kernel_size-1)//2, bias=False)def forward(self, x):out = F.relu(self.conv(x))out = torch.cat((x, out), 1)return out# 卷积 做了填充输出与输入尺寸相同
class ConvLayer(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride):super(ConvLayer, self).__init__()reflection_padding = kernel_size // 2# 边缘填充 上下左右分别reflection_padding行self.reflection_pad = nn.ReflectionPad2d(reflection_padding)self.conv2d = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride)def forward(self, x):out = self.reflection_pad(x)out = self.conv2d(out)return out# 上采样
class UpsampleConvLayer(torch.nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride):super(UpsampleConvLayer, self).__init__()# 反卷积 output=(input-1)*stride+outputpadding-2*padding+kernelsize 按照一下计算 output= 2input-2-2+4=2input# ConvTranspose2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, output_padding=0, groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1)self.conv2d = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=stride)def forward(self, x):out = self.conv2d(x)return out# resnet残差块
class ResidualBlock(torch.nn.Module):def __init__(self, channels):super(ResidualBlock, self).__init__()self.conv1 = ConvLayer(channels, channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1)self.conv2 = ConvLayer(channels, channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1)self.relu = nn.PReLU()def forward(self, x):residual = xout = self.relu(self.conv1(x))out = self.conv2(out) * 0.1out = torch.add(out, residual)return out
2.DFF密集特征融合结构图和代码
# fusion1为例注释下面语句
# 编码模块中的DFF密集功能融合模块 论文中对应深紫色块
class Encoder_MDCBlock1(torch.nn.Module):# num_filter:输入通道数=32 num_ft:循环次数=2def __init__(self, num_filter, num_ft, kernel_size=4, stride=2, padding=1, bias=True, activation='prelu', norm=None, mode='iter1'):super(Encoder_MDCBlock1, self).__init__()self.mode = mode# num_ft=1self.num_ft = num_ft - 1self.up_convs = nn.ModuleList()self.down_convs = nn.ModuleList()# 从0到1不包含1 也就是说i=0 一次循环for i in range(self.num_ft):self.up_convs.append(# 上采样 尺寸扩大两倍 通道数缩减两倍 通道数(32,16) up_convs模型只添加了一个反卷积DeconvBlock(num_filter//(2**i), num_filter//(2**(i+1)), kernel_size, stride, padding, bias, activation, norm=None))self.down_convs.append(# 下采样 通道数扩大两倍 尺寸缩小两倍 通道数(16,32) down_convs模型只添加了一个卷积ConvBlock(num_filter//(2**(i+1)), num_filter//(2**i), kernel_size, stride, padding, bias, activation, norm=None))# fusion1为例注释下面语句# ft_l:res2x:bs 32 240 320 ft_h_list:feature_mem = [res1x]:bs 16 480 640def forward(self, ft_l, ft_h_list):# 主干网络用的iter2if self.mode == 'iter2':# ft_fusion = res2x 是下采样后的特征图ft_fusion = ft_l# 从0到1不包含1 也就是说i=0 一次循环for i in range(len(ft_h_list)):# ft = res2xft = ft_fusion# num_ft=1 i=0 num_ft-i=1 也就是说j=0 一次循环for j in range(self.num_ft - i):# ft = res2x进行一次上采样 恢复到res1相同的尺寸ft = self.up_convs[j](ft)# ft_h_list:feature_mem = [res1x]# ft=up(res2)-res1ft = ft - ft_h_list[i]# num_ft=1 i=0 num_ft-i=1 也就是说j=0 一次循环for j in range(self.num_ft - i):# print(j)# num_ft-i-j-1=0 也就是一次下采样 ft=down(up(res2)-res1)ft = self.down_convs[self.num_ft - i - j - 1](ft)# ft_fusion=res2x+down(up(res2)-res1) :bs 32 240 320ft_fusion = ft_fusion + ftreturn ft_fusion
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import math# 3*3卷积 包含卷积批归一化和激活 步长为1 填充1 则输出的图像宽高尺寸不改变
# 属于编码网络的第一层卷积
class ConvBlock(torch.nn.Module):def __init__(self, input_size, output_size, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True, activation='prelu', norm=None):super(ConvBlock, self).__init__()self.conv = torch.nn.Conv2d(input_size, output_size, kernel_size, stride, padding, bias=bias)self.norm = normif self.norm =='batch':self.bn = torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(output_size)elif self.norm == 'instance':self.bn = torch.nn.InstanceNorm2d(output_size)self.activation = activationif self.activation == 'relu':self.act = torch.nn.ReLU(True)elif self.activation == 'prelu':self.act = torch.nn.PReLU()elif self.activation == 'lrelu':self.act = torch.nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)elif self.activation == 'tanh':self.act = torch.nn.Tanh()elif self.activation == 'sigmoid':self.act = torch.nn.Sigmoid()def forward(self, x):if self.norm is not None:out = self.bn(self.conv(x))else:out = self.conv(x)if self.activation != 'no':return self.act(out)else:return out# 反卷积+批归一化+激活
# 4*4反卷积 output=(input-1)*stride+outputpadding-2*padding+kernelsize 按照一下计算 output= 2input-2-2+4=2input
# ConvTranspose2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, output_padding=0, groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1)
class DeconvBlock(torch.nn.Module):def __init__(self, input_size, output_size, kernel_size=4, stride=2, padding=1, bias=True, activation='prelu', norm=None):super(DeconvBlock, self).__init__()self.deconv = torch.nn.ConvTranspose2d(input_size, output_size, kernel_size, stride, padding, bias=bias)self.norm = normif self.norm == 'batch':self.bn = torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(output_size)elif self.norm == 'instance':self.bn = torch.nn.InstanceNorm2d(output_size)self.activation = activationif self.activation == 'relu':self.act = torch.nn.ReLU(True)elif self.activation == 'prelu':self.act = torch.nn.PReLU()elif self.activation == 'lrelu':self.act = torch.nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)elif self.activation == 'tanh':self.act = torch.nn.Tanh()elif self.activation == 'sigmoid':self.act = torch.nn.Sigmoid()def forward(self, x):if self.norm is not None:out = self.bn(self.deconv(x))else:out = self.deconv(x)if self.activation is not None:return self.act(out)else:return outclass Decoder_MDCBlock1(torch.nn.Module):def __init__(self, num_filter, num_ft, kernel_size=4, stride=2, padding=1, bias=True, activation='prelu', norm=None, mode='iter1'):super(Decoder_MDCBlock1, self).__init__()self.mode = modeself.num_ft = num_ft - 1self.down_convs = nn.ModuleList()self.up_convs = nn.ModuleList()for i in range(self.num_ft):self.down_convs.append(ConvBlock(num_filter*(2**i), num_filter*(2**(i+1)), kernel_size, stride, padding, bias, activation, norm=None))self.up_convs.append(DeconvBlock(num_filter*(2**(i+1)), num_filter*(2**i), kernel_size, stride, padding, bias, activation, norm=None))def forward(self, ft_h, ft_l_list):if self.mode == 'iter1' or self.mode == 'conv':ft_h_list = []for i in range(len(ft_l_list)):ft_h_list.append(ft_h)ft_h = self.down_convs[self.num_ft- len(ft_l_list) + i](ft_h)ft_fusion = ft_hfor i in range(len(ft_l_list)):ft_fusion = self.up_convs[self.num_ft-i-1](ft_fusion - ft_l_list[i]) + ft_h_list[len(ft_l_list)-i-1]if self.mode == 'iter2':ft_fusion = ft_hfor i in range(len(ft_l_list)):ft = ft_fusionfor j in range(self.num_ft - i):ft = self.down_convs[j](ft)ft = ft - ft_l_list[i]for j in range(self.num_ft - i):ft = self.up_convs[self.num_ft - i - j - 1](ft)ft_fusion = ft_fusion + ftif self.mode == 'iter3':ft_fusion = ft_hfor i in range(len(ft_l_list)):ft = ft_fusionfor j in range(i+1):ft = self.down_convs[j](ft)ft = ft - ft_l_list[len(ft_l_list) - i - 1]for j in range(i+1):# print(j)ft = self.up_convs[i + 1 - j - 1](ft)ft_fusion = ft_fusion + ftif self.mode == 'iter4':ft_fusion = ft_hfor i in range(len(ft_l_list)):ft = ft_hfor j in range(self.num_ft - i):ft = self.down_convs[j](ft)ft = ft - ft_l_list[i]for j in range(self.num_ft - i):ft = self.up_convs[self.num_ft - i - j - 1](ft)ft_fusion = ft_fusion + ftreturn ft_fusion# fusion1为例注释下面语句
# 编码模块中的DFF密集功能融合模块 论文中对应深紫色块
class Encoder_MDCBlock1(torch.nn.Module):# num_filter:输入通道数=32 num_ft:循环次数=2def __init__(self, num_filter, num_ft, kernel_size=4, stride=2, padding=1, bias=True, activation='prelu', norm=None, mode='iter1'):super(Encoder_MDCBlock1, self).__init__()self.mode = mode# num_ft=1self.num_ft = num_ft - 1self.up_convs = nn.ModuleList()self.down_convs = nn.ModuleList()# 从0到1不包含1 也就是说i=0 一次循环for i in range(self.num_ft):self.up_convs.append(# 上采样 尺寸扩大两倍 通道数缩减两倍 通道数(32,16) up_convs模型只添加了一个反卷积DeconvBlock(num_filter//(2**i), num_filter//(2**(i+1)), kernel_size, stride, padding, bias, activation, norm=None))self.down_convs.append(# 下采样 通道数扩大两倍 尺寸缩小两倍 通道数(16,32) down_convs模型只添加了一个卷积ConvBlock(num_filter//(2**(i+1)), num_filter//(2**i), kernel_size, stride, padding, bias, activation, norm=None))# fusion1为例注释下面语句# ft_l:res2x:bs 32 240 320 ft_h_list:feature_mem = [res1x]:bs 16 480 640def forward(self, ft_l, ft_h_list):if self.mode == 'iter1' or self.mode == 'conv':ft_l_list = []for i in range(len(ft_h_list)):ft_l_list.append(ft_l)ft_l = self.up_convs[self.num_ft- len(ft_h_list) + i](ft_l)ft_fusion = ft_lfor i in range(len(ft_h_list)):ft_fusion = self.down_convs[self.num_ft-i-1](ft_fusion - ft_h_list[i]) + ft_l_list[len(ft_h_list)-i-1]# 主干网络用的iter2if self.mode == 'iter2':# ft_fusion = res2x 是下采样后的特征图ft_fusion = ft_l# 从0到1不包含1 也就是说i=0 一次循环for i in range(len(ft_h_list)):# ft = res2xft = ft_fusion# num_ft=1 i=0 num_ft-i=1 也就是说j=0 一次循环for j in range(self.num_ft - i):# ft = res2x进行一次上采样 恢复到res1相同的尺寸ft = self.up_convs[j](ft)# ft_h_list:feature_mem = [res1x]# ft=up(res2)-res1ft = ft - ft_h_list[i]# num_ft=1 i=0 num_ft-i=1 也就是说j=0 一次循环for j in range(self.num_ft - i):# print(j)# num_ft-i-j-1=0 也就是一次下采样 ft=down(up(res2)-res1)ft = self.down_convs[self.num_ft - i - j - 1](ft)# ft_fusion=res2x+down(up(res2)-res1) :bs 32 240 320ft_fusion = ft_fusion + ftif self.mode == 'iter3':ft_fusion = ft_lfor i in range(len(ft_h_list)):ft = ft_fusionfor j in range(i+1):ft = self.up_convs[j](ft)ft = ft - ft_h_list[len(ft_h_list) - i - 1]for j in range(i+1):# print(j)ft = self.down_convs[i + 1 - j - 1](ft)ft_fusion = ft_fusion + ftif self.mode == 'iter4':ft_fusion = ft_lfor i in range(len(ft_h_list)):ft = ft_lfor j in range(self.num_ft - i):ft = self.up_convs[j](ft)ft = ft - ft_h_list[i]for j in range(self.num_ft - i):# print(j)ft = self.down_convs[self.num_ft - i - j - 1](ft)ft_fusion = ft_fusion + ftreturn ft_fusion
3.SOS boosting module结构图和代码
# SOS boosting module 按照论文里的公式# res16x=res8x=bs 128 60 80# 对应论文大图把SOS boosting module图倒过来看# in=res8 jn+1=res16x res8x-res16x=res8xres8x = torch.add(res16x, res8x)res8x = self.dense_4(res8x) + res8x - res16x
4.剩余总体结构图和代码
代码如下(示例):
class Net(nn.Module):def __init__(self, res_blocks=18):super(Net, self).__init__()# 四次下采样 四次特征堆叠# 编码模块:第一层: 单步卷积 尺寸不变 论文中对应灰色块self.conv_input = ConvLayer(3, 16, kernel_size=11, stride=1)# 编码模块:第二层: 三个残差块 论文中对应黄色块16self.dense0 = nn.Sequential(ResidualBlock(16),ResidualBlock(16),ResidualBlock(16))# 编码模块:第三层: 步幅为2卷积 下采样同时通道双倍扩张 论文中对应浅紫色块self.conv2x = ConvLayer(16, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=2)# 编码模块:第四层:DFF密集功能融合模块 论文中对应深紫色块self.fusion1 = Encoder_MDCBlock1(32, 2, mode='iter2')# 编码模块:第五层:三个残差块 论文中对应黄色块32self.dense1 = nn.Sequential(ResidualBlock(32),ResidualBlock(32),ResidualBlock(32))# 编码模块:第六层: 步幅为2卷积 下采样同时通道双倍扩张 论文中对应浅紫色块self.conv4x = ConvLayer(32, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=2)# 编码模块:第七层:DFF密集功能融合模块 论文中对应深紫色块self.fusion2 = Encoder_MDCBlock1(64, 3, mode='iter2')# 编码模块:第八层:三个残差块 论文中对应黄色块64self.dense2 = nn.Sequential(ResidualBlock(64),ResidualBlock(64),ResidualBlock(64))# 编码模块:第九层:步幅为2卷积 下采样同时通道双倍扩张 论文中对应浅紫色块self.conv8x = ConvLayer(64, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=2)# 编码模块:第十层:DFF密集功能融合模块 论文中对应深紫色块self.fusion3 = Encoder_MDCBlock1(128, 4, mode='iter2')# 编码模块:第十一层:三个残差块 论文中对应黄色块128self.dense3 = nn.Sequential(ResidualBlock(128),ResidualBlock(128),ResidualBlock(128))# 编码模块:第十二层:步幅为2卷积 下采样同时通道双倍扩张 论文中对应浅紫色块self.conv16x = ConvLayer(128, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=2)# 编码模块:第十三层:DFF密集功能融合模块 论文中对应深紫色块self.fusion4 = Encoder_MDCBlock1(256, 5, mode='iter2')#self.dense4 = Dense_Block(256, 256)# Gresself.dehaze = nn.Sequential()# res_blocks=18 循环18个残差for i in range(0, res_blocks):self.dehaze.add_module('res%d' % i, ResidualBlock(256))# 四次下上采样# 解码模块:第一层上采样 三次残差块 密集功能融合模块self.convd16x = UpsampleConvLayer(256, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=2)self.dense_4 = nn.Sequential(ResidualBlock(128),ResidualBlock(128),ResidualBlock(128))self.fusion_4 = Decoder_MDCBlock1(128, 2, mode='iter2')# 解码模块:第二层上采样 三次残差块 密集功能融合模块self.convd8x = UpsampleConvLayer(128, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=2)self.dense_3 = nn.Sequential(ResidualBlock(64),ResidualBlock(64),ResidualBlock(64))self.fusion_3 = Decoder_MDCBlock1(64, 3, mode='iter2')# 解码模块:第三层上采样 三次残差块 密集功能融合模块self.convd4x = UpsampleConvLayer(64, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=2)self.dense_2 = nn.Sequential(ResidualBlock(32),ResidualBlock(32),ResidualBlock(32))self.fusion_2 = Decoder_MDCBlock1(32, 4, mode='iter2')# 解码模块:第四层上采样 三次残差块 密集功能融合模块self.convd2x = UpsampleConvLayer(32, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=2)self.dense_1 = nn.Sequential(ResidualBlock(16),ResidualBlock(16),ResidualBlock(16))self.fusion_1 = Decoder_MDCBlock1(16, 5, mode='iter2')# 单步卷积self.conv_output = ConvLayer(16, 3, kernel_size=3, stride=1)def forward(self, x):# Genc# 单步卷积 bs 3 480 640 -> bs 16 480 640res1x = self.conv_input(x)# res1x:bs 16 480 640feature_mem = [res1x]# 单步卷积的结果和残差块结果相加 x=bs 16 480 640x = self.dense0(res1x) + res1x# 第一次下采样 密集功能融合模块 残差块链接# bs 16 480 640 -> bs 32 240 320res2x = self.conv2x(x)# res2x:bs 32 240 320 -> bs 32 240 320res2x = self.fusion1(res2x, feature_mem)# feature_mem=[res1x,res2x] res2x:bs 32 240 320feature_mem.append(res2x)# bs 32 240 320 -> bs 32 240 320res2x =self.dense1(res2x) + res2x# 第二次下采样 密集功能融合模块 残差块链接# bs 32 240 320 -> bs 64 120 160res4x =self.conv4x(res2x)# res4x:bs 64 120 160 -> bs 64 120 160res4x = self.fusion2(res4x, feature_mem)# feature_mem=[res1x,res2x,res4x] res4x:bs 64 120 160feature_mem.append(res4x)# bs 64 120 160 -> bs 64 120 160res4x = self.dense2(res4x) + res4x# 第三次下采样 密集功能融合模块 残差块链接# bs 64 120 160 -> bs 128 60 80res8x = self.conv8x(res4x)# res8x: bs 128 60 80 -> bs 128 60 80res8x = self.fusion3(res8x, feature_mem)# feature_mem=[res1x,res2x,res4x,res8x]res8x: bs 128 60 80feature_mem.append(res8x)# bs 64 120 160 -> bs 128 60 80res8x = self.dense3(res8x) + res8x# 第四次下采样 密集功能融合模块 残差块链接# bs 128 60 80 -> bs 256 30 40res16x = self.conv16x(res8x)# res16x:bs 256 30 40res16x = self.fusion4(res16x, feature_mem)#res16x = self.dense4(res16x)# Gresres_dehaze = res16x# 特征图乘以2in_ft = res16x*2# 循环18个残差 + res16x*2 - res16xres16x = self.dehaze(in_ft) + in_ft - res_dehaze# feature_mem=[res1x,res2x,res4x,res8x,res16x]res16x: bs 256 30 40feature_mem_up = [res16x]# Gdec# 第一层上采样 三次残差块 密集功能融合模块# bs 256 30 40 -> bs 128 61 81res16x = self.convd16x(res16x)# F.upsample参数:输入 尺寸 插值方法# res16x:bs 128 61 81 -> bs 128 60 80res16x = F.upsample(res16x, res8x.size()[2:], mode='bilinear')# SOS boosting module 按照论文里的公式# res16x=res8x=bs 128 60 80# 对应论文大图把SOS boosting module图倒过来看# in=res8 jn+1=res16x res8x-res16x=res8xres8x = torch.add(res16x, res8x)res8x = self.dense_4(res8x) + res8x - res16x# DFFres8x = self.fusion_4(res8x, feature_mem_up)# feature_mem=[res1x,res2x,res4x,res8x,res16x,res8x]feature_mem_up.append(res8x)# 第二层上采样 三次残差块 密集功能融合模块# bs 128 60 80 -> bs 64 121 161res8x = self.convd8x(res8x)# bs 64 121 161 -> bs 64 120 160res8x = F.upsample(res8x, res4x.size()[2:], mode='bilinear')# SOS boosting moduleres4x = torch.add(res8x, res4x)res4x = self.dense_3(res4x) + res4x - res8x# DFFres4x = self.fusion_3(res4x, feature_mem_up)# feature_mem=[res1x,res2x,res4x,res8x,res16x,res8x,res4x]feature_mem_up.append(res4x)# 第三层上采样 三次残差块 密集功能融合模块# bs 64 120 160 -> bs 32 241 321res4x = self.convd4x(res4x)# bs 32 241 321 -> bs 32 240 320res4x = F.upsample(res4x, res2x.size()[2:], mode='bilinear')# SOS boosting moduleres2x = torch.add(res4x, res2x)res2x = self.dense_2(res2x) + res2x - res4x# DFFres2x = self.fusion_2(res2x, feature_mem_up)# feature_mem=[res1x,res2x,res4x,res8x,res16x,res8x,res4x,res2x]feature_mem_up.append(res2x)# 第四层上采样 三次残差块 密集功能融合模块# bs 32 240 320 -> bs 16 481 641res2x = self.convd2x(res2x)# bs 16 481 641 -> bs 16 480 640res2x = F.upsample(res2x, x.size()[2:], mode='bilinear')# SOS boosting modulex = torch.add(res2x, x)x = self.dense_1(x) + x - res2x# DFFx = self.fusion_1(x, feature_mem_up)# bs 16 480 640 -> bs 3 480 640x = self.conv_output(x)return x
八、Transformer去雾文献(无代码只有网络结构图)
1.U2-Former 一个用于图像恢复的嵌套的u形Transformer
2.Hybrid Local-Global Transformer混合局部全局Transformer
2.读入数据
代码如下(示例):
data = pd.read_csv('https://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/1283/adult.data.csv')
print(data.head())
该处使用的url网络请求的数据。
总结
提示:这里对文章进行总结:
例如:以上就是今天要讲的内容,本文仅仅简单介绍了pandas的使用,而pandas提供了大量能使我们快速便捷地处理数据的函数和方法。